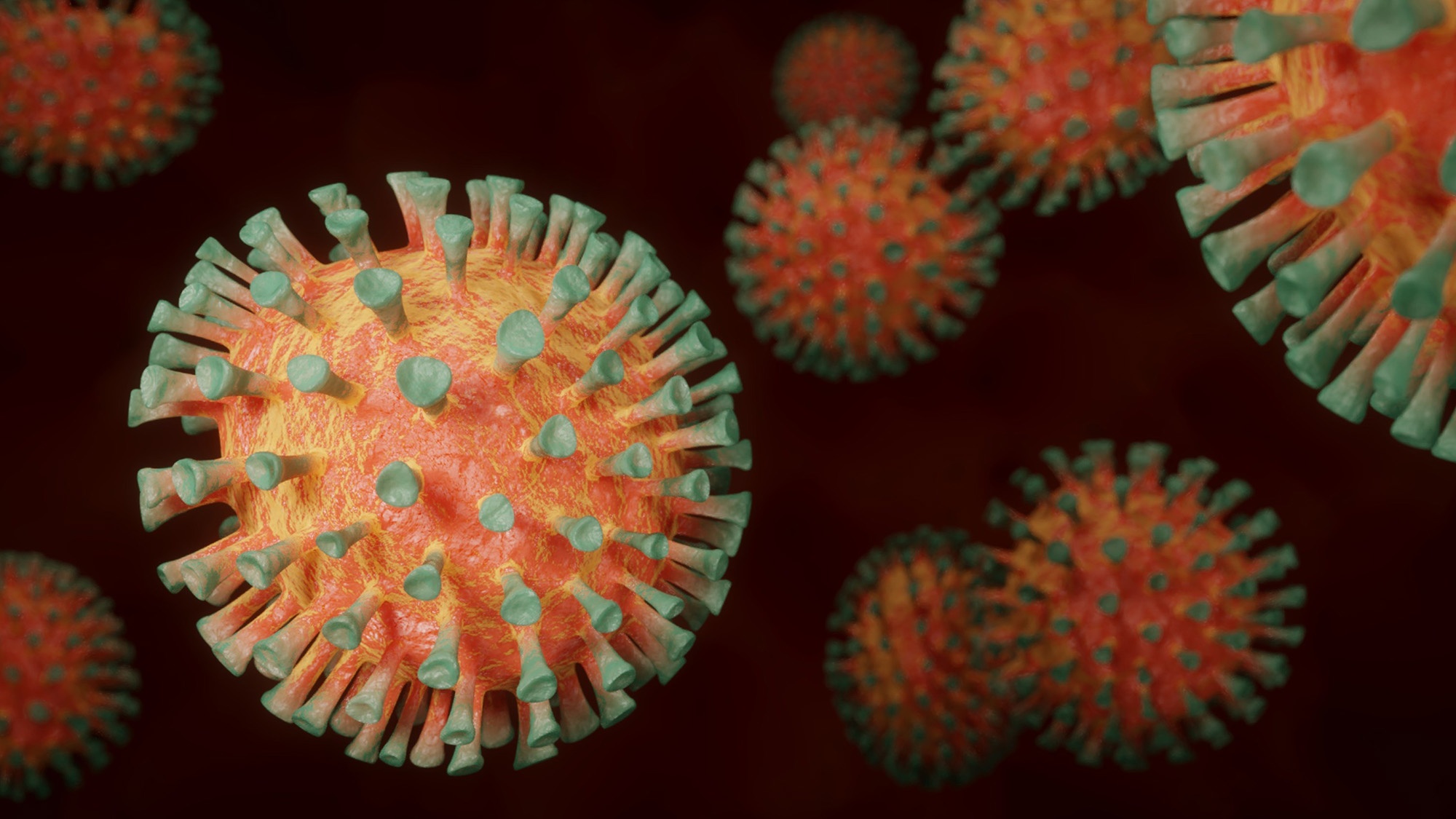
Scientists in Spain say they have discovered a type of glass and a type of clay that have antiviral properties and are capable of destroying viruses including COVID-19 in 10 minutes.
The Spanish scientists, from the Higher Centre for Scientific Research (CSIC; ‘Centro Superior de Investigaciones Científicas’), have reportedly confirmed that both of the materials eliminate 99 percent of the virus’ infection capabilities.

The glass and clay with the virucidal properties also said to be low-cost and could be used to decontaminate surfaces, liquids and even the air of viral particles.
The materials are said to technically be a type of soda-lime glass, which is an umbrella term for the most common type of glass in the world, and a clay that is called kaolin. Kaolin is a type of clay that is found in the wild and that is often used in medicine, notably to stop bleeding.
There is also hope that these materials could be used to create antiviral drugs with little to no toxicity because they are inorganic materials.
So far, the new materials have reportedly been tested against COVID-19, influenza, herpes simplex and adenoviruses, and they are also reportedly effective against bacteria and fungi.

Belen Cabal, a researcher at the Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology Research Center (CINN; ‘Centro de Investigacion en Nanomateriales y Nanotecnologia’), said: “These materials are capable of significantly inhibiting microbiological growth, whether of bacterial, fungal or viral origin, and are perfectly compatible with living beings and the environment.”
The results of the research have been published in the multidisciplinary academic journal Material Today Bio.
The research is the result of collaboration between scientists from CINN, CSIC-University of Oviedo-Principality of Asturias) and the CEU University Saint Paul. Experts from the University of Navarra and the Complutense University of Madrid also participated in the research. The research project was led by the CSIC.

To find out more about the author, editor or agency that supplied this story – please click below.
Story By: Joseph Golder, Sub-Editor: James King, Agency: Newsflash
The Ananova page is created by and dedicated to professional, independent freelance journalists. It is a place for us to showcase our work. When our news is sold to our media partners, we will include the link here.