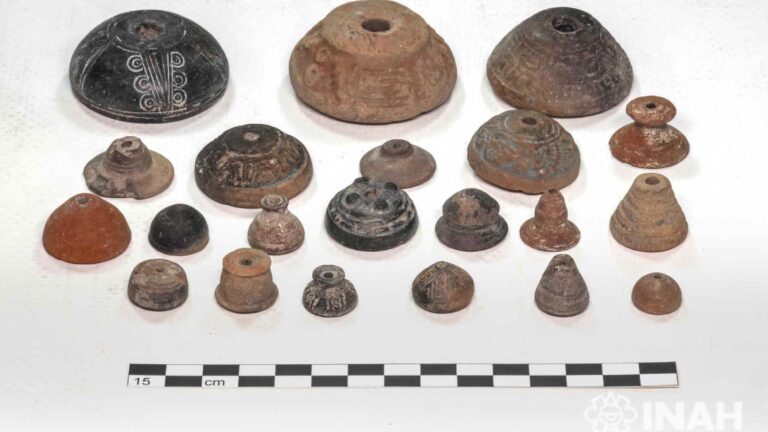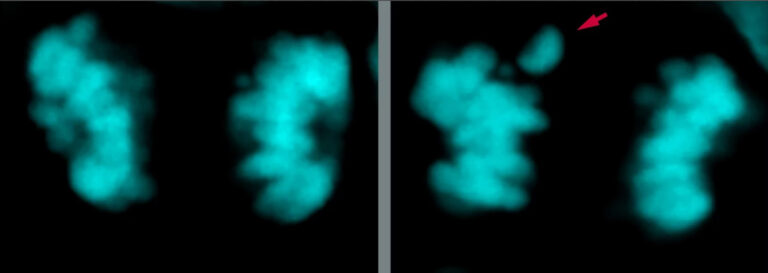
Modern Human Brains Less Error-Prone Than Neanderthals, Says Study
Modern human brains make fewer mistakes than those of Neanderthals despite being of similar size, scientists in Germany have found. Researchers from the German Max Planck Institute have discovered that…