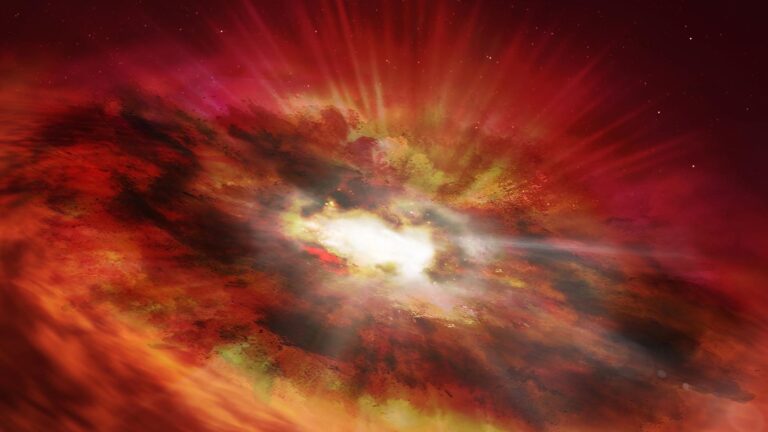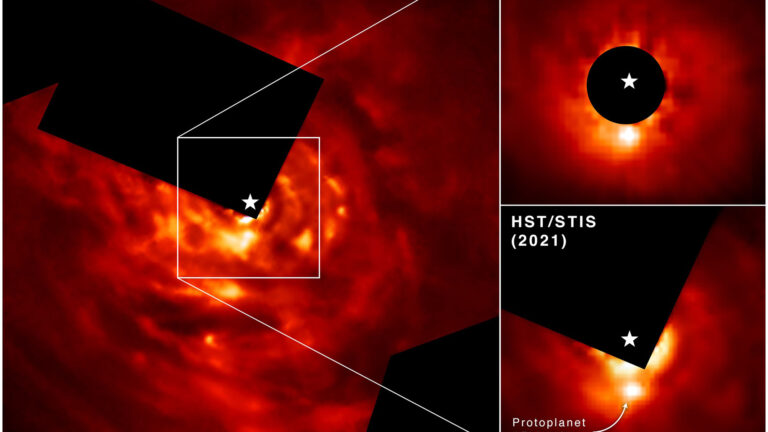
Researchers were able to directly image newly forming exoplanet AB Aurigae b over a 13-year span using Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) and its Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrograph (NICMOS). In the top right, Hubble’s NICMOS image captured in 2007 shows AB Aurigae b in a due south position compared to its host star, which is covered by the instrument’s coronagraph. The image captured in 2021 by STIS shows the protoplanet has moved in a counterclockwise motion over time. (NASA, ESA, Thayne Currie (Subaru Telescope, Eureka Scientific Inc./Newsflash)
A massive new planet, nine times the size of Jupiter, is being formed in an intense and violent process, as recorded by NASA’s Hubble space telescope, challenging understandings about planetary…





